Sustainability in the UAE: Navigating the Path of Corporate Social Responsibility and Development Regulations
Sustainability in the UAE: Navigating the Path of Corporate Social Responsibility and Development Regulations
In recent years, the UAE has positioned itself as a leader in sustainability and social responsibility, marking a significant shift in the corporate landscape. This transformation aligns with the government’s commitment to environmental protection, social development, and a prosperous, inclusive economy. Initiatives like UAE Vision 2021, the UAE Green Agenda 2030, and the National Climate Change Plan 2050 reflect the country's ambition to meet global sustainability goals. However, when examining the UAE’s regulatory framework for corporate social responsibility (CSR) and sustainable development, it becomes evident that a comparison with European regulations reveals key areas for improvement and alignment with international standards.
UAE’s Regulatory Framework: Laying the Groundwork for Sustainable Development
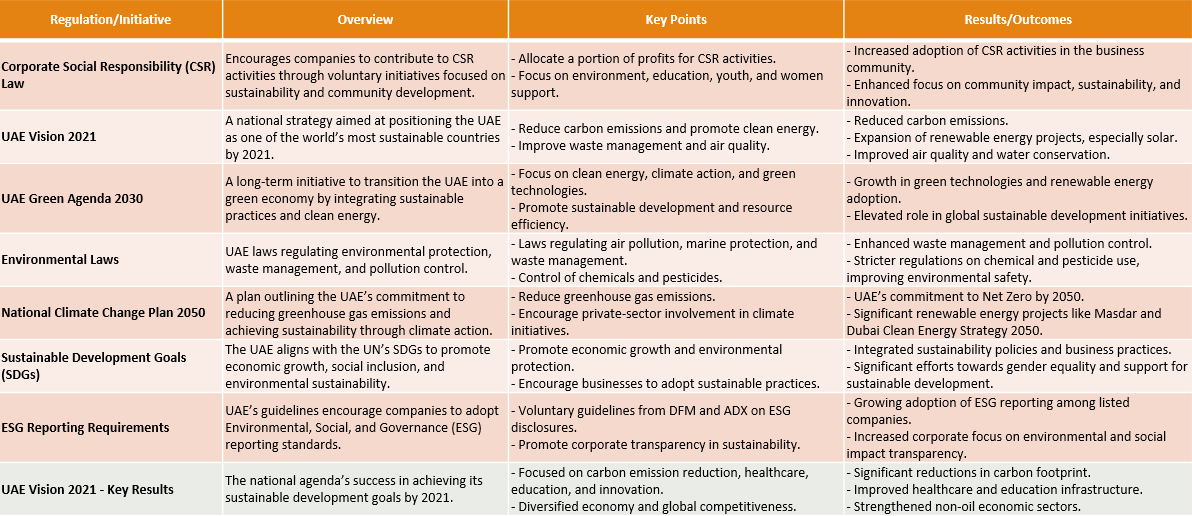
The UAE's dedication to sustainability is evident in its various laws and national strategies aimed at promoting social responsibility, environmental protection, and economic diversification. These frameworks encourage businesses to contribute voluntarily to the nation’s sustainability goals. A cornerstone of the UAE’s sustainability agenda is Federal Law No. 2 of 2015 concerning Commercial Companies, which encourages businesses to allocate a portion of their profits to CSR activities. Key focus areas include environmental sustainability, education, innovation, community development, and support for youth and women. While participation remains voluntary, this law is increasingly adopted as a best practice across sectors.
Central to this transformation is UAE Vision 2021, which aspires to position the nation as one of the world's most sustainable countries by reducing carbon emissions, increasing clean energy usage, and promoting waste reduction. Following this vision, the UAE Green Agenda 2030 establishes a comprehensive framework for transitioning to a green economy, outlining five strategic objectives to guide sustainable practices across industries.
In addition to these overarching frameworks, specific environmental laws, such as Federal Law No. 24 of 1999 and Federal Law No. 20 of 2006, aim to protect natural resources and regulate pollution. These laws showcase the UAE's commitment to environmental protection while promoting sustainable business practices. The National Climate Change Plan 2050 further highlights the UAE's ambition to lead climate action in the region by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, enhancing climate resilience, and encouraging private sector participation in achieving these objectives.
However, stark differences arise when comparing the UAE's regulatory approach to that of Europe. While the UAE has laid a foundation for sustainable development, Europe’s regulatory landscape is far more stringent, comprehensive, and mandatory.
Europe’s Leadership in CSR and Sustainability Regulations
Europe has long been recognized as a global leader in establishing CSR and sustainability regulations. Mandatory CSR reporting has been a hallmark of the European approach, exemplified by laws such as the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD). This directive requires large public companies to disclose their CSR and sustainability activities. Starting in 2024, the updated Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) will expand this requirement to include all large companies and those listed on regulated markets, increasing transparency and holding businesses accountable for their environmental and social impact.
Additionally, the EU Green Deal aims to make Europe the first climate-neutral continent by 2050. This ambitious framework addresses carbon emissions, promotes resource efficiency, and integrates circular economy principles into Europe’s economic policies. Legislative advancements such as the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) and the Circular Economy Action Plan ensure that companies operate within environmentally sustainable limits and contribute to long-term climate goals.
Europe’s stringent environmental regulations also require businesses to account for their impact on the environment. The EU Climate Law, enacted in 2021, enshrines the goal of Net Zero emissions by 2050 into legislation, while the Circular Economy Action Plan encourages businesses to reduce waste, reuse materials, and implement sustainable production methods.
Contrasts Between the UAE and Europe: Voluntary vs. Mandatory Approaches
The primary distinction between the regulatory landscapes of the UAE and Europe lies in the voluntary nature of CSR participation in the UAE, contrasted with Europe’s mandatory frameworks. While the UAE encourages CSR engagement through platforms like the CSR Smart Platform and laws such as Federal Law No. 2 of 2015, participation remains optional. In contrast, Europe’s NFRD, CSRD, and EU Green Deal impose strict disclosure requirements and compliance with sustainability regulations, with penalties for non-compliance.
Comparative Analysis of Social Responsibility and Sustainable Development Regulations in the UAE and Europe
Similarly, the UAE's environmental laws are more flexible. While the National Climate Change Plan 2050 sets ambitious targets for Net Zero emissions, enforcement mechanisms are less rigid than those in Europe, where non-compliance incurs significant financial penalties. Although the UAE demonstrates a commitment to align with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through national strategies like the Green Agenda 2030, Europe has advanced further in SDG integration across sectors, particularly in ESG investment. The EU Taxonomy Regulation defines environmentally sustainable activities, creating a clear pathway for businesses and investors to prioritize green projects, while ESG reporting in the UAE remains largely voluntary.
Actions the UAE Can Take to Strengthen its Sustainability Framework
To better align with Europe’s leadership in CSR and sustainability, the UAE could consider the following actions:
Introduce Mandatory CSR Reporting: Transitioning from voluntary to mandatory CSR reporting for large companies, akin to Europe’s NFRD and CSRD frameworks, would enhance transparency and accountability while ensuring businesses actively contribute to national sustainability goals.
Strengthen Environmental Regulations and Enforcement: Implementing stricter regulations on emissions, pollution, and waste management, along with clearer penalties for non-compliance, would encourage businesses to reduce their carbon footprint while aligning with global standards.
Expand ESG Integration and Disclosure: Formalizing ESG reporting requirements for publicly listed companies would foster sustainable practices and increase transparency, attracting ESG-focused investors to the UAE.
Encourage Green Investments and Sustainable Finance: Establishing frameworks for green bonds and sustainable finance could mobilize capital toward eco-friendly projects, accelerating the transition to a green economy.
Promote Circular Economy Principles: Introducing policies that prioritize reducing waste and optimizing resource use would encourage businesses to adopt sustainable production and consumption methods.
Enhance Worker Rights and Social Responsibility: Strengthening worker protections and formalizing gender equality policies in corporate governance would align the UAE with Europe’s progressive labor and human rights standards.
Looking Ahead: The UAE’s Potential as a Sustainability Leader
The UAE’s ambitions are clear—through its Net Zero 2050 commitment, National Climate Change Plan, and a growing focus on renewable energy, the country is making substantial strides toward becoming a global leader in sustainability. However, as evidenced by Europe’s experience, comprehensive, mandatory regulations and frameworks will be vital to solidifying the UAE’s role as a sustainability powerhouse.
In this context, MEBAS, a partner for the UAE with IRDO, offers the International Certification Course for Social Responsibility and Sustainable Development Managers. This course is designed to equip participants with the comprehensive knowledge and practical skills necessary to integrate effective social responsibility and sustainability practices into their organizations.
🔗 Ready to enhance your CSR expertise and contribute to a sustainable future? Secure your spot and get more information by filling out the form here: 🔗 https://lnkd.in/dqcr3qrA
By adopting stricter regulations, mandatory reporting, and incentives for sustainable business practices, the UAE can achieve its climate goals and position itself as a regional leader in responsible business. Collaboration between public and private sectors, alongside robust international partnerships, will be essential for driving long-term change and ensuring the UAE’s success in building a sustainable, socially responsible future.